南湖新闻网讯(通讯员 郑侃)近日,我校工学院夏俊芳教授团队研究成果以“Effects of vibration parameters on the interfacial adhesion system between soil and metal surface”为题在Soil & tillage research发表。研究揭示了简谐激励下土壤-机具界面粘附系统的振动脱附机理,为长江中下游农业区耕整机械减粘脱附、减阻降耗研究提供了新思路。
长江中下游农业区土壤黏重板结,耕整机械作业时触土部件易粘附土壤,导致作业质量降低、阻耗增加。因此,如何解决土壤粘附问题成为耕整机械研究的重点。研究表明,机械振动可有效减少土壤粘附。
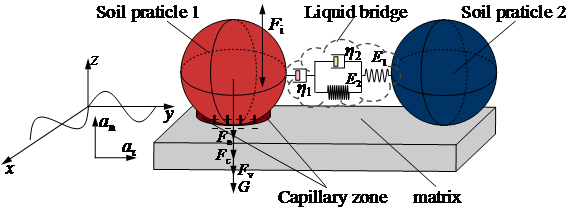
土壤振动脱附物理模型
该研究为探究振幅、振动频率和振动时间等振动特性参数对切向、法向界面粘附系统振动脱附效果的影响,搭建一套振动脱附试验装置,并构建土壤-机具界面粘附系统振动脱附动力学模型。

界面不同时刻振动脱附状态
通过单因素与正交试验,得到振动脱附率与振动特性参数间的数学模型;依据极值理论对模型寻优与验证,得出切向振动最优参数组合为振幅7.99g,振动频率42.87Hz,振动时间26.03s;法向振动脱附率最优参数组合为振幅9.00g,振动频率59.76Hz,振动时间88.20s。研究结果可为长江中下游农业区振动耕整机械研发与性能提升提供数据支撑。
华中农业大学工学院博士研究生刘国阳为论文第一作者,郑侃老师为通讯作者。该研究得到国家自然科学基金、公益性行业(农业)科研专项和国家重点研发计划子课题等项目资助。
审核人:明庭庆
【英文摘要】
In actual preparation of arable lands, the soil easily adheres to soil-engaging components of tillage machinery and affects the plowing efficiency and quality, thus leading to low traction efficiency and high power consumption. It has been proposed that vibration can effectively reduce the adhesion of soils to the soil-engaging components in field operation. Here, in order to explore the vibration response characteristics of soils and the mechanism for soil detachment under sine wave vibration, a vibration detachment measurement system of soils was assembled with an acceleration sensor, an electric vibration generator, a power amplifier and a data acquisition system. The measurement system was then used to study the effects of three vibration characteristic parameters (amplitude, frequency and time) on the interfacial adhesion system between soil and metal surface (ASSM) in both tangential and normal directions. Taking the soil detachment rate as a representative characteristic of ASSM, the effect of each factor was analyzed through single-factor experiments. The optimal interval of each vibration parameter was determined based on the experiment results. According to the orthogonal experimental design and analysis, we established a mathematical model for the relationship between the vibration soil detachment rate and the vibration parameters, as well as identified their primary and secondary order and interaction effect on the soil detachment rate. As determined by response surface analysis, the optimal combination of parameters for soil detachment rate in the tangential direction is vibration amplitude of 7.99 g, vibration frequency of 42.87 Hz and vibration time of 26.03 s, and that in the normal direction is vibration amplitude of 9.00 g, vibration frequency of 59.76 Hz and vibration time of 88.20 s. The relative errors of the optimization results are 1.05% and 2.65%, respectively, which are generally consistent with the prediction results of regression equation. These results indicate that the mathematical model can be used to predict and evaluate soil adhesion under vibration. Therefore, the soil detachment performance of ASSM can be enhanced by a reasonable setting of vibration parameters, which may be of great significance for improving the working quality and efficiency of tillage machinery.

