南湖新闻网讯(通讯员 寇萌)近日,我校资源与环境学院土壤化学与环境团队在在水稻田土壤重金属污染风险评估及精准修复方面取得新进展,相关成果分别发表于环境类期刊Journal of Hazardous Materials和Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety上。
水稻作为中国主要粮食作物,吸收了土壤中Cd等重金属,使其面临较严重的粮食安全问题。水稻往往易吸收土壤中生物有效态Cd,而土壤pH值和多种金属离子共存对Cd形态分布有显著影响。鉴于水稻土高异质性和复杂性,尚缺乏Cd与其它金属的交互作用对水稻毒性的影响、应用于区域尺度水稻土Cd生物有效性及其关联的水稻食品安全等预测研究。
基于此,我校土壤化学与环境团队耦合多表面模型(MSM)和地理信息系统(GIS)技术实现县域尺度水稻-土壤系统中生物有效性Cd预测,进一步构建了一套基于水稻食品安全的pH调控图(图1),从而实现县域尺度石灰材料修复土壤Cd污染的精准施用技术。基于三种分析场景,本研究量化了pH对Cd生物有效性的影响贡献,显示有87.51% Cd生物有效变异解释率,并结合pH提升建议值和石灰材料施用量计算器,绘制了Cd污染修复石灰材料精确施用量地图,对研究区域水稻土Cd污染风险评估提出了有效措施。该研究结果可为重金属污染土壤修复提供精准修复策略,也可作为评估水稻土重金属环境风险的重要工具。
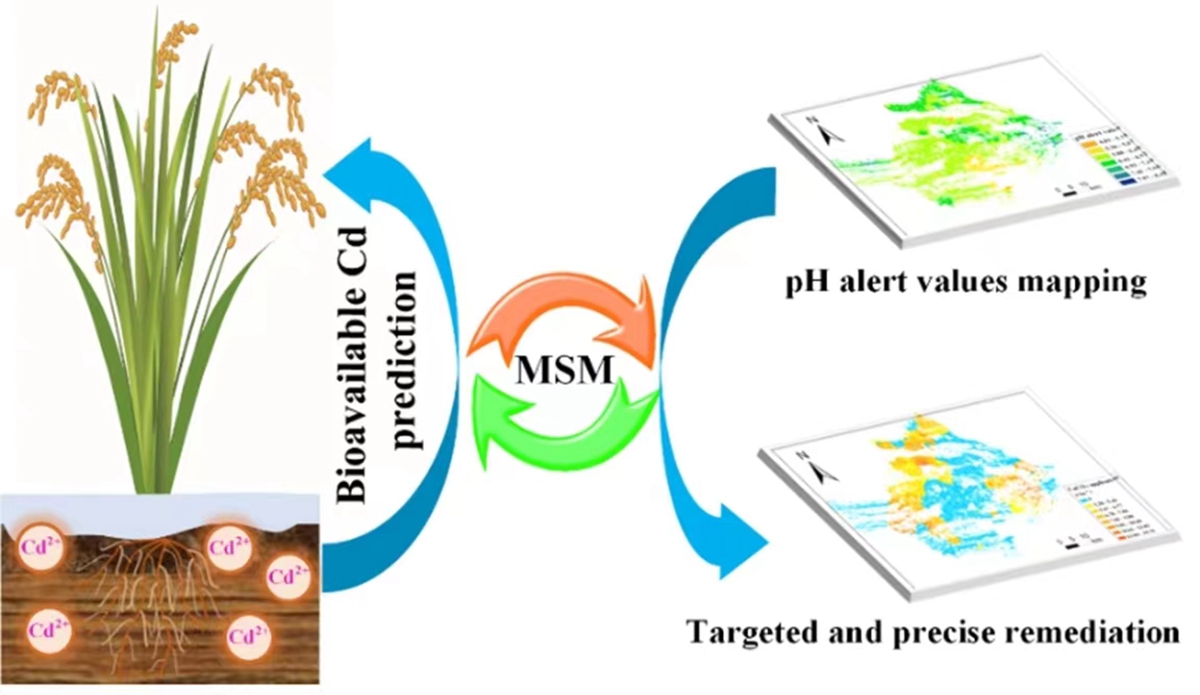
图1 基于MSM的重金属Cd生物有效性预测与精准修复
此外,土壤化学与环境团队结合浓度相加(CA)模型、独立作用(IA)模型和多元回归树分析(MRT),建立了镉、铅复合污染对水稻毒害的定量分析体系(图2)。研究结果表明Pb-Cd间的交互作用均能减弱Pb和Cd的毒性,其中Cd对Pb毒性的抑制作用显著;Pb-Cd复合浓度相近时,Pb和Cd相互作用对水稻根系伸长具有显著的拮抗作用;在低Pb浓度(Cd > 0.0195, Pb < 0.015 mg/L),对水稻根系有协同作用;高浓度Pb (Cd < 0.225, Pb ≥ 1.25 mg/ L),Pb对水稻根系的毒性主要为Pb。该研究首次提出了评价不同剂量水平下重金属相互作用行为的系统方法,可为制定农田重金属复合污染控制标准提供方法参考。
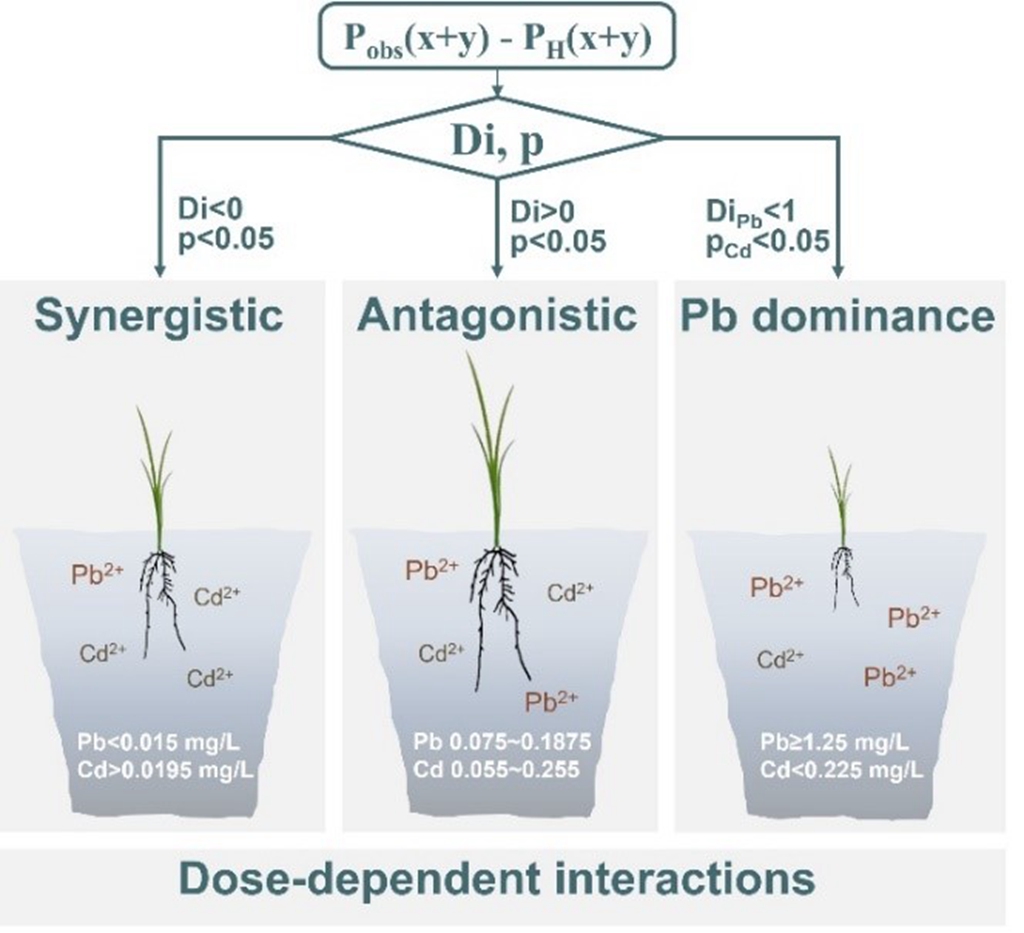
图2 Pb-Cd复合污染对水稻根伸长的剂量主导交互作用行为
论文第一作者分别为博士生杨正论、寇萌,汪明霞教授为通讯作者,我校谭文峰教授、侯静涛副研究员、刘朝阳副教授、熊娟副教授等也参与了该项研究。本研究得到自然科学基金项目,中央高校基本科研业务费专项资金和湖北省自然科学基金项目等资助。
【英文摘要】
Relative to total cadmium (Cd) content, bioavailable Cd in paddy soil is regarded as a more reasonable indicator for the risk of Cd bioaccumulation in rice. However, there is still a lack of approach to accurately predict the content of bioavailable Cd in paddy soil due to its heterogeneity and complexity. Here, multi-surface speciation model (MSM) was employed to predict the bioavailable Cd and Cd immobilization effect. Moreover, a precise remediation strategy was designed based on screening and scenario simulation of the sensitive factors with MSM. The results demonstrated that MSM can well predict Cd bioaccumulation risk in rice. The contribution of pH to Cd bioavailability was quantified under three analysis scenarios, accounting for 87.51% of the total variance of bioavailable Cd. In addition, the pH alert value (6.31 ± 0.52) for Cd risk was acquired for each rice field on a county scale. A precise map for the application amount of lime materials was constructed by taking CaCO3 (3.38–15.75 t ha-1) as a recommended economical and green immobilization agent. This study provides a potentially effective approach for risk assessment of Cd contamination in rice and important reference for precise Cd remediation in paddy soil.
【原文链接】
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2023.130963
【英文摘要】
Combined pollution of cadmium (Cd) and lead (Pb) occurs frequently in agriculture lands, which has received increasing research attention. However, little is known about the interaction behaviors of Cd and Pb at various concentrations in the mixture. This study evaluated the single and combined effects of Cd and Pb on rice (Oryza sativa L.) root elongation through acute exposure test. The combined pollution was analyzed with the concentration addition (CA) model, independent action (IA) model and mathematical statistical methods. The dose-response results revealed that the interaction could weaken the toxicity of both Pb and Cd, and Cd had a more significant inhibitory effect on Pb toxicity. The predicted values of CA and IA models were consistently lower than the observed values in the relative root elongation range of 0%–60%. Further, combining the CA or IA model with mathematical statistical methods, the interaction of Pb and Cd at similar concentrations showed a significant antagonistic effect on rice root elongation. At low Pb concentrations (Cd > 0.0195, Pb < 0.015 mg/L), there was a synergistic effect of the mixture on rice root; at high Pb concentrations (Cd < 0.225, Pb ≥ 1.25 mg/L), Pb dominated the toxicity on rice root. This is the first report of a systematic method for assessing heavy metal interaction at different concentration levels, which may facilitate the formulation of control standards of heavy metal combined pollution in agricultural land.
【原文链接】
https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2023.114622
审核人:汪明霞
