南湖新闻网讯(通讯员 丁星)近日,我校理学院陈浩教授带领的先进材料与绿色催化科研团队在ACS Catalysis发表题为“Dual-site Synergetic Photochemical Activation of Chlorinated Phenols Triggered by Surface Hydroxyls of photocatalysts under Visible Light”的研究论文,该研究报道了氯酚类污染物在表面羟基修饰的光催化材料上活化和降解的作用机制。
多氯酚化合物是一类廉价且高效的除虫剂或杀菌剂,但其过度施用造成的环境污染十分严重。多氯酚污染物具有高毒、生物累积和环境持久性等特征,在生态环境中的迁移和转化备受关注。光化学降解是多氯酚非生物降解过程中最重要的途径之一,其中半导体矿物表面羟基光化学活化多氯酚的环境行为更是普遍存在。深入研究有机污染物在表面羟基上的光化学活化和降解过程是当前环境领域研究的前沿和热点问题。
鉴于此,我校先进材料与绿色催化团队利用氨水热处理法制备出富含表面羟基的光催化材料,以期揭示不同类型表面羟基光化学活化多氯酚的作用机制。通过DFT理论计算和原位红外光谱研究了五氯酚钠在不同类型表面羟基(端接羟基和桥接羟基)上的吸附和活化机理。如图1a所示,表面桥接和端接羟基的双位点结构能够分别提供吸附和反应位点,在多氯酚光化学吸附和活化过程中表现出高效协同作用,促进五氯酚钠的高效脱氯解毒和降解矿化。利用气相色谱-质谱联用技术对五氯酚钠降解路径分析发现,表面羟基光化学活化的五氯酚钠更容易发生羟基化脱氯过程,进而实现高效脱氯解毒和降解矿化(图1b)。此外,作者发现表面羟基介导的污染物光化学活化策略具有普适性,广泛适用于各种氯酚污染物,甚至是酚类污染物。该工作为深入理解氯酚类污染物在富表面羟基矿物界面的吸附、迁移和光化学活化机制提供理论依据。
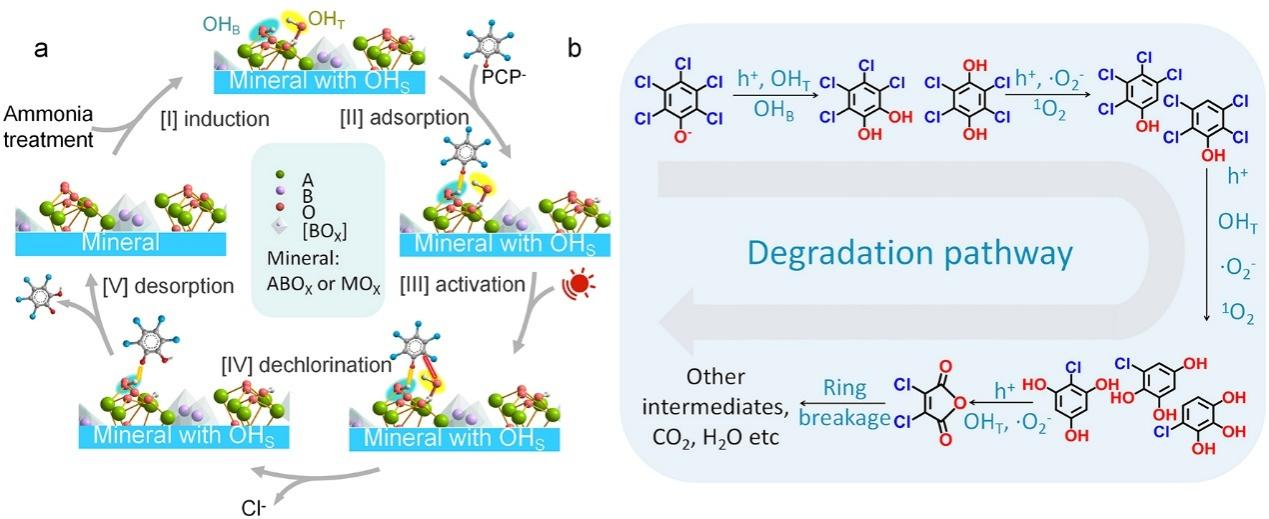
图1 不同表面羟基介导的五氯酚降解机理图
我校理学院已毕业博士研究生徐骁为论文第一作者,理学院陈浩教授和丁星副教授为论文通讯作者。该研究得到了国家自然科学基金和武汉市曙光计划等项目的支持。
【英文摘要】
In this study, abundant surface bridging hydroxyls and terminal hydroxyls are deliberately and cyclicly introduced in multiple photocatalysts via a facile hydrothermal method in ammonia for figuring out how these typical surface hydroxyls function in chlorinated phenols (CPs) photochemical decomposition process. Experimental and theoretical results unveil that the photochemical reaction between CPs and surface hydroxyls is a dextrous pathway for the dechlorination and degradation of CPs on Bi2MoO6 as well as other similar metal oxide minerals. The bridging hydroxyls mainly serve as adsorption sites to capture CPs with the formation of adsorbed CPs species (CPs*), while the adjacent terminal hydroxyls predominantly act as active sites and generate active hydroxyls to attack the CPs* under visible light. This dual-site synergetic activation triggered by surface hydroxyls markedly enhanced the effective dechlorination and photochemical decomposition of CPs. This present work well extends the scope of CPs photochemical transformation process at a molecular level.
文章链接:https://pubs.acs.org/doi/full/10.1021/acscatal.3c00189
审核人:陈 浩
